Data reigns supreme in today’s business landscape. Among all the metrics and analytics, firmographic data stands out as a cornerstone for strategic decision-making. These insights offer a clear picture of B2B markets and customers, helping companies shape their product, marketing and sales strategies based on their audience’s needs.
In this article, you’ll learn everything you need to know about firmographic data, including its definition and benefits, firmographic segmentation, and the various ways to collect company data.
What is firmographic data?
Firmographic data is a set of characteristics that define businesses and organizations. Similar to how demographics outline the characteristics of individuals, firmographics delve into the traits of companies. These traits include industry type, company size, revenue, location, organizational structure and more.
By looking at firmographic data, you can get a comprehensive snapshot of a company and understand its role in the market. Then, you can leverage this information to make strategic business decisions, whether it’s determining the look and feel of your brand, identifying prospective customers to sell to, or making adaptations to your product.
Note that you may hear other terms for firmographic data as well, such as emporographics, firm demographics, business demographics or company demographics. All these terms can be used interchangeably and encompass the company characteristics we’ll discuss below.
Firmographic data examples
The main business characteristics that make up firmographic data include:
- Industry type: Classifies businesses into specific sectors such as healthcare, technology, finance, manufacturing or retail.
- Company size: Includes metrics such as the number of employees, categorizing businesses as small, medium or large enterprises.
- Revenue: Indicates the financial performance of a company, allowing for firmographic segmentation based on revenue brackets.
- Funding: Tracks the financing history of businesses, including seed funding, Series A, Series B and subsequent rounds, reflecting their growth trajectory and investor interest. Take a look at this list of companies with recent Series A or Series B funding.
- Geographic location: Specifies the physical location of businesses, including country, region, state, city and postal code.
- Years in operation: Indicates the longevity of a business, which can be crucial for understanding its stability and experience in the industry.
- Hiring and layoffs data: Offers valuable indicators of the company’s financial health, reflecting its ability to invest in talent and scale. You can get layoffs data from the Crunchbase layoffs tracker.
- Leadership team: Indicates the composition of the company’s leadership, including executives, department heads and key decision-makers. The hiring of new leadership can signify new, strategic initiatives and indicate confidence in the company’s future growth and financial stability.
- Organizational structure: Describes the hierarchy and structure of companies, including subsidiaries, divisions and corporate affiliations.
- Ownership type: Identifies whether a business is privately owned, publicly traded, government-owned or a non-profit organization.
- Customer base: Profiles the types of customers served by a business, including demographics, industries and purchasing behaviors.
- Tech stack: Describes the technology and tools a company uses, such as CRM systems and cloud services, providing insights into its digital infrastructure and potential technology needs.
- Market presence: Indicates the market share, competitive positioning and brand recognition of businesses within their respective industries.
- Financial performance: Evaluates key financial metrics such as profitability, liquidity, solvency and growth trends over time.
- Business lifecycle stage: Identifies whether a business is newly growing, maturing or declining, influencing its strategic priorities and resource allocation.

Why is firmographic data important?
So, what’s the purpose in gathering all this data? Public and private company data help you better understand your B2B customers, allocate resources more effectively, identify growth and revenue opportunities, and stay competitive. In fact, there are a huge number of benefits of gathering firmographic data:
- Market segmentation: Collecting firmographic data allows for market segmentation based on industry verticals, company size, revenue and other parameters, enabling businesses to develop tailored marketing strategies for each segment.
- Improved sales strategies: Understanding the firmographic makeup of potential customers allows sales teams to tailor their approaches and pitches to resonate more effectively with different segments, leading to higher conversion rates.
- Enhanced lead generation: By leveraging firmographic data, sales and marketing teams can generate high-quality leads that match a company’s ideal customer profiles.
- Competitive analysis: Analyzing the firmographic data of your competitors provides valuable insights into their strengths, weaknesses, market positioning and customer base, helping your business refine its own competitive strategy.
- Risk assessment: Firmographic data allows you to assess the financial stability and risk associated with potential business partners, customers or suppliers, helping mitigate potential risks and losses.
Benefits of firmographic segmentation
Let’s go back to the first benefit we mentioned above: market segmentation. One of the main ways B2B companies use firmographic data is to divide their target audience into distinct segments based on their shared characteristics.
This process — called firmographic segmentation — helps companies identify commonalities among their target audience, such as industry type, company size, geographic location or recent funding.
Dividing target customers into distinct groups helps you adapt your marketing efforts, sales pitches and product offerings to address the specific needs and preferences of each segment. This allows your business to focus its resources more effectively, deliver personalized experiences to prospective customers, and prioritize high-potential prospects when making business decisions.
Firmographic segmentation examples
Let’s look at some examples of firmographic segmentation that organizations use to reach and engage with their customer base:
- Industry-based segmentation: Companies may segment their target market based on industry verticals such as healthcare, technology or finance. This segmentation allows businesses to tailor their marketing messages and solutions to address the unique challenges and requirements of each industry.
- Company size segmentation: Targeting customers based on company size, such as small businesses, mid-sized enterprises and large corporations, enables organizations to offer products and services that align with the scale and complexity of their operations.
- Geographic segmentation: Geographic segmentation divides the market into different regions based on geographic factors. Businesses can customize their marketing strategies and promotions to resonate with the cultural, economic and demographic characteristics of each location.
- Revenue-based segmentation: Segmenting customers based on revenue brackets or financial metrics allows businesses to prioritize high-value accounts and tailor pricing, discounts and incentives accordingly.
Key firmographic questions
Now that you know what firmographic data and segmentation are, you might be ready to start gathering company information yourself. Create a specific set of questions you can answer to guide your research. Use these questions as a jumping off point, and feel free to customize them based on your goals:
- What industry is the company operating in?
- What is the size of the company?
- Where is the company located?
- What is the ownership structure of the company?
- What technologies and systems does the company use?
- Who are the key decision-makers and influencers within the company?
- What is the company’s financial health?
- How does the company compare to competitors in the market?
- What growth opportunities and challenges does the company face?
- What is the company’s reputation and brand perception?
How to gather firmographic data
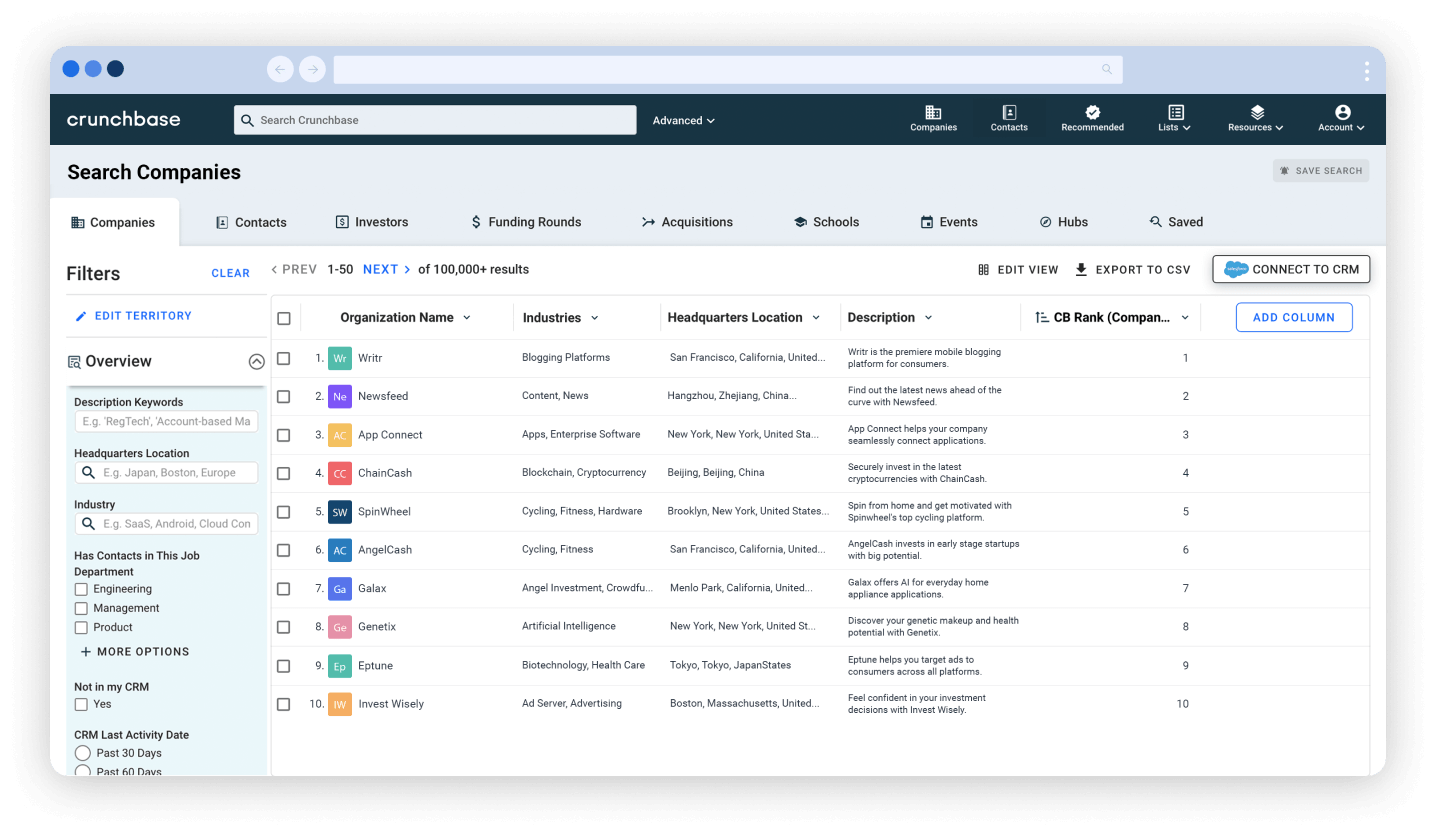
You can gather firmographic data using different sources and tools. One effective platform is Crunchbase, which offers data on private and public companies. This includes details about industry verticals, company location and size, funding rounds, mergers and acquisitions, key executives, layoffs and hiring data, tech stack and more. Using Crunchbase helps you identify companies with buying power, pinpoint the ones you want to research, partner with or sell to, and monitor their activity in real-time.
You can also collect firmographic data using primary research, like surveys, interviews and direct interactions with customers or industry experts. All this provides valuable firsthand insights into the firmographic makeup of target companies. Additionally, mining public databases, regulatory filings, industry reports and third-party data providers can enhance the depth and accuracy of your firmographic data collection.